- Ponatinib, a potent drug for blood cancer treatment, poses heart disease risks by triggering an integrated stress response (ISR) in heart cells.
- Researchers discovered that neutralizing ISR hyperactivation could mitigate ponatinib-induced cardiotoxicity without compromising its anti-tumor effects.
- The study, part of the growing field of cardio-oncology, highlights the importance of balancing oncology and cardiology in developing safer leukemia therapies.
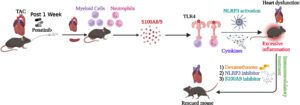
A recent study sheds light on the mechanism behind the cardiovascular risks associated with the blood cancer drug ponatinib. Led by Sang Ging Ong, the research reveals that ponatinib triggers an integrated stress response (ISR) in heart cells, leading to potential cardiotoxicity.
In the study published in Circulation Research, Ong and his team found that ponatinib activates a process called the integrated stress response, ultimately damaging heart cells responsible for contraction. This activation occurs through the kinase enzyme GCN2, which is paradoxically activated by ponatinib despite its role as a kinase inhibitor.
However, the study also offers a glimmer of hope by suggesting that neutralizing the integrated stress response could prevent or reverse ponatinib-induced cardiotoxicity without compromising its anti-tumor effects. While further research is needed to confirm these findings in human subjects, the study represents a crucial step in understanding and mitigating the cardiovascular risks associated with ponatinib treatment in blood cancer patients.














